

Previously only the stroke of the information age (elderly). Along with the time, there is a tendency that is now threatening stroke age even under the age of 45 years. The disease also appeared to stroke can strike anyone regardless of their position or socio-economic levels.
Here are some facts and reviews you need to know in order to increase vigilance against the threat of stroke at age:
1. Stroke, No.3 murderer in Indonesia
2. Recognize the type - Type of Stroke
3. Know Stroke Risk Factors
4. Reading Stroke Symptoms
5. Diagnose Stroke
6. Handling of Stroke
7. There is still hope better
8. Lifestyle, the spark of stroke
9. Expert Review of stroke
Stroke, No.3 murderer in Indonesia
Stroke case increased in developed countries like United States where obesity and junk food has been infecting. Based on statistical data in the United States, occur each year 750,000 new cases of stroke in the United States. The data shows that every 45 minutes, there is one person in the United States affected by the attack of stroke.
According to the Stroke Foundation of Indonesia (Yastroki), there is a tendency of increasing the number of stroke in Indonesia in the last decade. Kecenderungannya attack the young generation that is still productive. This will affect the level of productivity and the decrease can lead to social and economic terganggunya family.
Could not be denied that the increase in the number of stroke patients in Indonesia associated with outbreaks of obesity due to fat-rich meal pattern or the cholesterol in the whole world, not the exception of Indonesia.
In Indonesia, the disease is stroke number three after the death of heart and cancer. In fact, according to a survey in 2004, stroke is the No.1 killer in hospitals all over the government in Indonesia.
Estimated to have 500,000 people affected by stroke. Of these, third could recover, another third of the functional disturbances are light up and the remaining third of the weight of the functional disturbance that requires a patient continuously in the mattress.
Serebrovaskuler diseases including stroke (brain blood vessel), which marked the death of the brain network (infark serebral) happens because the reduced flow of blood and oxygen to the brain. WHO defines stroke is that the symptoms of nervous system function deficits caused by brain blood vessel disease and not by the other than that.
Recognizing Types of Stroke
 Type of Stroke
Type of Stroke divided into two types, namely
iskemik stroke and stroke hemorragik. On iskemik stroke, blood flow to the brain has stopped because aterosklerosis (cumulation cholesterol in the blood vessel wall), or blood clot that has a clog blood vessel to the brain. Most patients or 83% of the stroke type.
Stroke hemorragik, broken blood vessel so that obstruct the normal flow of blood and blood leak into an area in the brain and damaged. Almost 70 percent of stroke cases hemorrhagik occur in people with hypertension.
At the stroke iskemik, stoppage could occur in the blood vessel along the arterial routes leading to the brain. Blood to the brain supplied by the two karotis Interna arteria and two arterial vertebralis. Arterial-arterial is a branch of the aorta arch heart.

A ateroma (deposition of fat) can form in the arterial blood vessel karotis causing reduced blood flow. The situation is very serious because every blood vessel arterial karotis in normal circumstances to give blood to most of the brain. Deposition of fat can also be detached from the wall and the arterial flow in the blood, and arterial clog smaller.
Arterial blood vessel arterial karotis and vertebralis with percabangannya can also stopped because of a blood clot originating from elsewhere, for example, from the heart or one valve. This kind of stroke called serebral embolism (embolism sumbatan =, = serebral brain blood vessel), which most often occur in patients who undergo new heart surgery and heart valve patients aberration or heart rhythm disturbances (especially atrium fibrillation).
Fat embolism rarely cause stroke. If the form of fat embolism of fat from the bone marrow that is released into the broken blood flow and eventually join in an arterial.
Stroke can also occur when an infection causing inflammation or constriction of the blood vessel to the brain. Drugs (eg cocaine and amfetamin) also can narrow the blood vessel in the brain and cause a stroke.
Decrease in blood pressure that suddenly can cause reduced blood flow to the brain, which usually cause a person unconscious. Stroke can occur if blood pressure is very low weight and chronic. This occurs when someone has lost a lot of blood due to injury or surgery, heart attack or heart rhythm is abnormal.
Know Stroke Risk Factors Stroke
Stroke or circumstances which caused the stroke or called Stroke Risk Factors. Diseases mentioned above, among others, Hypertension, Heart Diseases, Diabetes Mellitus, Hiperlipidemia (elevation in blood lipid content). The condition can cause a stroke that is old age, Obesity, smoking, ethnic group (MaRia vega / Spain), gender (male), lack of exercise.
Reading Stroke Symptoms
Most cases of stroke occur suddenly, very quickly and cause brain damage in a few minutes (completed stroke). Then a stroke wither in a few hours to 1-2 days due to increased extent of the network of brain death (stroke in evolution).
Development of the disease usually (but not always) diselingi with a stable period, where the expansion of the network or dead stop while some improvements occurred. Stroke symptoms that appear depend on any part of the brain affected.
Reading cue stroke can be done with some of the symptoms of stroke following:
* Weakness or paralysis arm or leg or one of the body.

* The loss of some vision or hearing.
* Vision ganda.
* Pusing.
* Talk is not clear (rero).
* It's hard to think or say the words right.
* Not able to identify the part of the body.
* Unusual movements.
* Loss of bladder control.
* Imparity and drop.
* Fainting.
Neurologis aberration that resulted from the attack of stroke can be more serious or more extensive, dealing with coma or stupor and are settled. In addition, the stroke can cause depression, or the inability to control emotions.
Stroke can also cause brain swelling or edema. This is dangerous because the space in the skull is limited. Pressure that can arise further brain damage and aggravate network neurologis aberration, although strokenya itself does not grow large.
Diagnose Stroke
Diagnosis stroke was builded usually based on the results of the disease and physical examination. Physical examination can help determine the location of damage to the brain. There are two types of imaging examination techniques (pencitraan) to evaluate the cases of stroke or brain blood vessel disease (Cerebrovascular Disease / CVD), the Computed Tomography (CT scan) and Magnetic resonance Imaging (MRI).
CT scan imaging known as the most simple, fast and relatively inexpensive for the case of stroke. However, in some cases, CT scan is less sensitive than MRI, for example, in the case of stroke hiperakut.
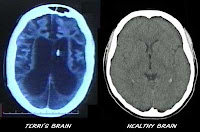
To strengthen the diagnosis is usually made examination MRI or CT scan. Both the examination can also help determine the cause of stroke, bleeding, or whether the brain tumor. Sometimes made, namely the determination of the order angiografi blood vessel / lymph through kapilaroskopi or fluoroskopi.
Handling of Stroke respiratory a stroke attack, immediately do the examination to determine whether the causes of blood clot or bleeding that can not be corrected with drugs not clot.
Recent research shows that paralysis and other symptoms can be prevented or restored if recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (RTPA) or streptokinase that function given the clot within 3 hours after the occurrence of stroke.
Antikoagulan also does not usually given to people with high blood pressure and is never given to patients with brain haemorrhage because akan add to the risk of the occurrence of bleeding in the brain.
Stroke patients are usually given oxygen and installed infus to enter the liquid and food substances. At the stroke in evolution given antikoagulan (eg, heparin), but the medicine is not given if there has been completed stroke.
Completed on the stroke, some brain dead network. Improve blood flow to the area will not be able to restore its function. Because it usually does not do surgery.
Appointment sumbatan vein after minor stroke or transient ischemic attack, in fact can reduce the risk of a stroke in the future. Around 24.5% patients experienced recurrent stroke.
To reduce the swelling and pressure in the brain in acute stroke patients, usually given manitol or kortikosteroid. Stroke patients who may require a very heavy respirator (breathing equipment bantu) to maintain the respiratory adekuat. In addition, special attention needs to function to the bladder, alimentary tract and skin (to prevent the occurrence of injury in the skin because of the emphasis).
Stroke usually does not stand on its own, so that when a physiological difference that must be treated for example, accompany the heart failure, heart rhythm is not regular, high blood pressure and infection of the lungs. After the attack of stroke, usually occur mood changes (especially depression), which can be corrected with medication or psychological therapy.
There is still hope for better
Rehabilitation of stroke about 30% -40% of stroke patients who can still heal perfectly provided with in a period of 6 hours or less. This is important so that patients do not experience disability. Even if there are symptoms such as the way the rest of the game or berbicaranya Pelo, but the rest of the symptoms of this can still be cured.

Unfortunately, most of the new stroke patients came to hospital 48-72 hours after the attack. If so, action needs to be done is the restoration. Recovery action is necessary to reduce complications due to stroke and attempt to restore the patient back to normal as before the attack of stroke.
Efforts to restore the health of stroke patients should be done as soon as possible, ideally starting 4-5 days after the patient's condition is stable. Each patient requires handling different, depending on the needs of the patient. This process takes about 6-12 days.
Life style, fuse Stroke Productive Age. Age is a risk factor of stroke, the risk of old age then was exposed to the higher strokenya. However, now the age need to be wary of the threat of stroke. At the age, stroke can strike, especially on those who like fatty foods and drugs (even if it does not yet have an exact number).

Junk foodLife style lifestyle is always the black sheep disease that attacks various age. Young people often apply the pattern of eating that is not often consumed with a healthy dishes are loaded with fat and cholesterol but low fiber.
Young people who travel the length of his life is still able to compete with berkiprah and human resources from abroad. Disability due to the clothing of their stroke, a burden not only families, but also burden the public in general.
Always better to prevent than treat. While stroke can still be prevented, why not try?
First, with the behavior of healthy living since early. Second, the control of risk factors must be optimal. Third, conduct medical check-up regularly and periodically, and the patient must recognize the early signs of stroke.
To prevent "the silent killer" and someone recommended this to reduce smoking, doing regular exercise, limiting alcoholic beverages, and avoid excessive stress.

 major damage to your health, your mood, your productivity, your relationships, and your quality of life.
major damage to your health, your mood, your productivity, your relationships, and your quality of life.

 reacts just as strongly as if you were facing a life-or-death situation. If you have a lot of responsibilities and worries, your emergency stress response may be “on” most of the time. The more your body’s stress system is activated, the easier it is to trip and the harder it is to shut off.
reacts just as strongly as if you were facing a life-or-death situation. If you have a lot of responsibilities and worries, your emergency stress response may be “on” most of the time. The more your body’s stress system is activated, the easier it is to trip and the harder it is to shut off.







 Previously only the stroke of the information age (elderly). Along with the time, there is a tendency that is now threatening stroke age even under the age of 45 years. The disease also appeared to stroke can strike anyone regardless of their position or socio-economic levels.
Previously only the stroke of the information age (elderly). Along with the time, there is a tendency that is now threatening stroke age even under the age of 45 years. The disease also appeared to stroke can strike anyone regardless of their position or socio-economic levels.






















